Melanoma is the deadliest type of skin cancer and one of the most common cancers of all types diagnosed in people around the world Rates of melanoma are rising rapidly, especially in younger people. In fact, cases of melanoma have tripled in the last 30 years, at a time when cancer rates for other common cancers have declined.
Its main cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light (UV) exposure (directly from the sun or from tanning devices) in individuals with low levels of the skin pigment melanin, and the malignancy develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. In women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men they most commonly occur on the back. About a quarter of them develop from moles — changes in a mole that can indicate melanoma include an increase in size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness or breakdown of the skin. Covering yourself up, using sunscreen and avoiding UV light can prevent the development of melanoma.
Early symptoms include changes to the shape or color of existing moles; they can easily be remembered from the first six letters of the English alphabet: Asymmetry; Borders (irregular with edges and corners); Color (variegated); Diameter (greater than 6 mm (0.24 in), about the size of a pencil eraser); Evolving over time; and Funny-looking. At later stages, the mole may itch, ulcerate or bleed.
There is now some good news from Israel about melanoma: A new
for melanoma in animal models, doubling the therapeutic effectiveness of medications and making possible a 30 percent reduction in dosage.
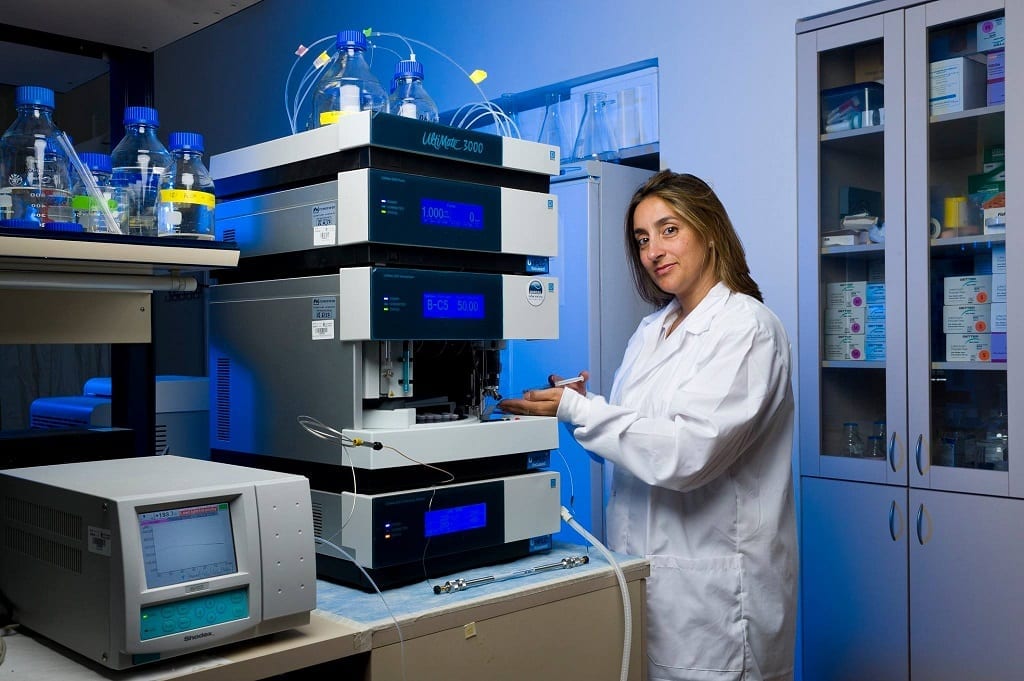
The researchers developed a polymeric nanocarrier that selectively delivers two medications and releases them simultaneously at the malignant target. The combined medications, packed into the nanocarrier, were up to 2.5 times more effective than treatment in control groups. In addition, the combined nanomedicine achieves the same therapeutic effect with a significantly lower dose compared to free medications administered without the nanoparticle.
The researchers at Tel Aviv University, led by Prof. Ronit Satchi-Fainaro from the department of physiology and pharmacology at the Sackler School of Medicine, included doctoral students Evgeni Pisarevsky, Dr. Rachel Blau and Yana Epshtein. The paper was published as the cover article of the August 2020 issue of Advanced Therapeutics and entitled: “Rational Design of Polyglutamic Acid Delivering an Optimized Combination of Drugs Targeting Mutated BRAF and MEK in Melanoma.”
The innovative system delivers the drugs to their target safely and accurately without causing any damage to healthy tissues. In this way, it significantly enhances effectiveness, enables dose reduction, and prevents side effects.
The team developed an innovative nanotechnological drug delivery system that significantly enhances the effectiveness of treatment for the aggressive melanoma. The nanocarrier is a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer made up of repeating units of glutamic acids (PGA or polyglutamic acid), packaging together two biological drugs belonging to different families with proven efficacy for the treatment of melanoma –BRAF inhibitors (Dabrafenib) and MEK inhibitors (Selumetinib, approved for use in children with NF1 – neurofibromatosis type I).
Satchi-Fainaro noted that “one of the major obstacles of the biological treatments is that after a while, the cancer cells develop resistance to the drugs. We assume that by precise delivery of two or more targeted drugs that will attack the cancer cells forcefully and simultaneously from different directions, we can delay or even prevent the acquisition of this drug-resistance.”
“Targeted therapies against cancer can relieve symptoms and induce remission; however, they often present limited duration of disease control, cause side effects, and may induce acquired resistance,” they wrote. “Therefore, there is great motivation to develop a unique delivery system, targeted to the tumor, in which several active entities can be combined, the therapeutic index can be increased by reducing systemic exposure, and their synergistic activity can be enhanced.
In this project, “we looked for a solution to a problem often associated with drug cocktails,” she continued. “Today, most oncological treatments are administered in the form of cocktails of several medications. But despite the fact that all drugs are administered to the patient simultaneously, they do not reach the tumor at the same time, due to differences in basic parameters, such as how long they survive in the bloodstream (half-life), and the time it takes each drug to reach the tumor tissue. Thus, in most cases, the medications do not work concurrently, which prevents them from attaining optimal synergistic activity.”
Responding to these challenges, the researchers developed an innovative, efficient and biodegradable drug delivery system. Two biological drugs, known to be effective for the treatment of melanoma, Dabrafenib and Selumetinib, (inhibiting two different components –BRAF and MEK respectively – in the biological pathway that is over-activated in melanoma), were chosen, with the intention of delivering them jointly to the tumor by using a nanocarrier. The drug nanocarrier chosen for the task was PGA, a polymer of glutamic acid – one of nature’s most common amino acids. Developed in Satchi-Fainaro’s lab several years ago, the nanocarrier has already been tested successfully for treating pancreatic, breast and ovarian cancer in animal models.
First, the researchers determined the optimal ratio between the two medications – based on levels and types of toxicity, as well as the resistance mechanism developed by cancer cells for each medication – to ultimately ensure maximum effectiveness, minimal toxicity and optimal synergistic activity. Another important advantage of joint delivery is reduced dosage; a much lower dose is required compared to each drug when administered independently.
The next step was using chemical modifications to enable bonding between the polymeric carrier and the chosen drugs. This combined system can travel through the body with total safety, causing no damage to healthy tissues. Upon reaching the cancer cells, the nanocarrier encounters proteins of the cathepsins enzyme family, which are highly activated in malignant tumors. The proteins degrade the polymer, releasing the drugs which become active and join forces to attack the tumor. “It’s like several passengers riding in one cab and getting off together at the same address. They all arrive at the same destination, right at the same time,” she explained.
Tested on a mouse model of melanoma, the new treatment showed promising results – the nanocarrier delivered the two drugs to the tumor and released them there simultaneously in quantities about 20 times greater than those that reach the tumor when similar doses of the same medications are administered independently. In addition, the therapeutic effect achieved by the drugs delivered by the nanocarrier lasted much longer – two to two-and-a-half times compared to control group and the group treated with free medications.
According to the research team, this means that the new platform enables much lower dosages – about one third of the dose required in regular drug cocktails, and the treatment as a whole is both safer and more effective. Also, if needed, the new approach allows for dosages that are much higher than the maximum dosage permissible in current methods, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the treatment even further.
“In this project, we developed an innovative drug delivery system for treating melanoma, delivering two proven medications and releasing them simultaneously at the tumor site,” concluded Satchi-Fainaru.The treatment proved both safer and more effective than the same medications administered as a cocktail. Moreover, our new platform is highly modular and can be used for delivering a vast range of medications. We believe that its potential for enhancing therapeutics for different diseases is practically endless.”